Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course Details
Post Diploma Training in Cardiology. Mobile No: 01797-522136,01987-073965.Hotline:01969947171. Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Courses are PDT-Cardiology Course 6 Months, PDT-Cardiology Course 1 Year, PDT Cardiology Course 2 Years. 6 Months Course Fee 35,500/-, 1 Years Course Fee 70,500/-, 2 Years Course Fee 1,30,500/-.

Location of Post Diploma Training in Cardiology
Post Diploma Training in . Mobile Number.01987073965.01797522136,HotLine-01969947171 HRTD Medical Institute , Abdul Ali Madbor Mention, Section-6, Block-Kha, Road-1, Plot-11, Mirpur-10 (Gol-Chattar) Metro Rail Pilar NO-249, Dhaka-1216. It is situated by the West Side of Agrani Bank, the South Side of Fire Service, Islami Bank, Janata Bank, Social Islami Bank, Medinova, Ibrahim Diabetic Hospital, the North Side of Baitul Mamur Jame Mosjid, Grave of Baitul Mamur Jame Mosjid, and East Side of Maliha Apartment.
Hostel Facilities in HRTD Medical Institute
Hostel & Meal Facilities
The Institute has hostel facilities for the students. Students can take a bed in the hostel.
Hostel Fee Tk 3000/- Per Month
Meal Charges Tk 3000/- Per Month. ( Approximately )
হোস্টাল ও খাবার সুবিধা
ইনস্টিটিউটে শিক্ষার্থীদের জন্য হোস্টেল সুবিধা রয়েছে। ছাত্ররা হোস্টেলে বিছানা নিতে পারে।
হোস্টেল ফি 3000/- টাকা প্রতি মাসে,
খাবারের চার্জ 3000/- টাকা প্রতি মাসে।(প্রায়)
Course Fee for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 6 Months
Course Fee for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology 6 Months at HRTD Medical Institute. Admission Fee=15,500/-,Monthly Fee 3000×6=18,000/-,Exam Fee=2000, Total Course Fee=35,500/-.This Course Contains 4 Subjects .Exam Mark 400.
Course Fee for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 1 Year
Course Fee for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 1 Year at HRTD Medical Institute. Admission Fee=20,500/-,Monthly Fee 3500×12=42,000/-,Exam Fee=4000×2=8000, Total Course Fee=70,500/-.This Course Contains 8 Subjects .Exam Mark 800.
Course Fee for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 2 Years
Course Fee for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 2 Years at HRTD Medical Institute. Admission Fee=30,500/-,Monthly Fee 3500 x 24=84,000/-,Exam Fee=4000×4=16,000, Total Course. Fee=1,30,500/-.This Course Contains 16 Subjects .Exam Mark 1600.
Subjects for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 6 Months
This 6 Months Course contains 4 subjects. Mobile No: 01987073965.01797522136,HotLine-01969947171
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology
- Cardiovascular Drugs & Pharmacology
- Management of Hypertension & Hypotension
- Coronary circulation & Conductive system
Subjects for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 1 Year
This 1 Year Course contains 8 subjects. Mobile No: 01987073965.01797522136,HotLine-01969947171
1st Semester
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology
- Cardiovascular Drugs & Pharmacology
- Management of Hypertension & Hypotension
- Coronary circulation & Conductive system
2nd Semester
- Heart Block (Coronary & Conductive Block)
- Cardiac Arrhythmias & Corrections
- ECG for Medical Practice
- Cardiovascular Disease & Treatment
Subjects for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course 2 Years
This 2 Year Course contains 16 subjects. Mobile No: 01987073965.01797522136,HotLine-01969947171
1st Semester
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology
- Cardiovascular Drugs & Pharmacology
- Management of Hypertension & Hypotension
- Coronary circulation & Conductive system
2nd Semester
- Heart Block (Coronary & Conductive Block)
- Cardiac Arrhythmias & Corrections
- ECG for Medical Practice
- Cardiovascular Disease & Treatment
3rd Semester
4th Semester
Some Subjects Details for Post Diploma Training in Cardiology Course Given Below
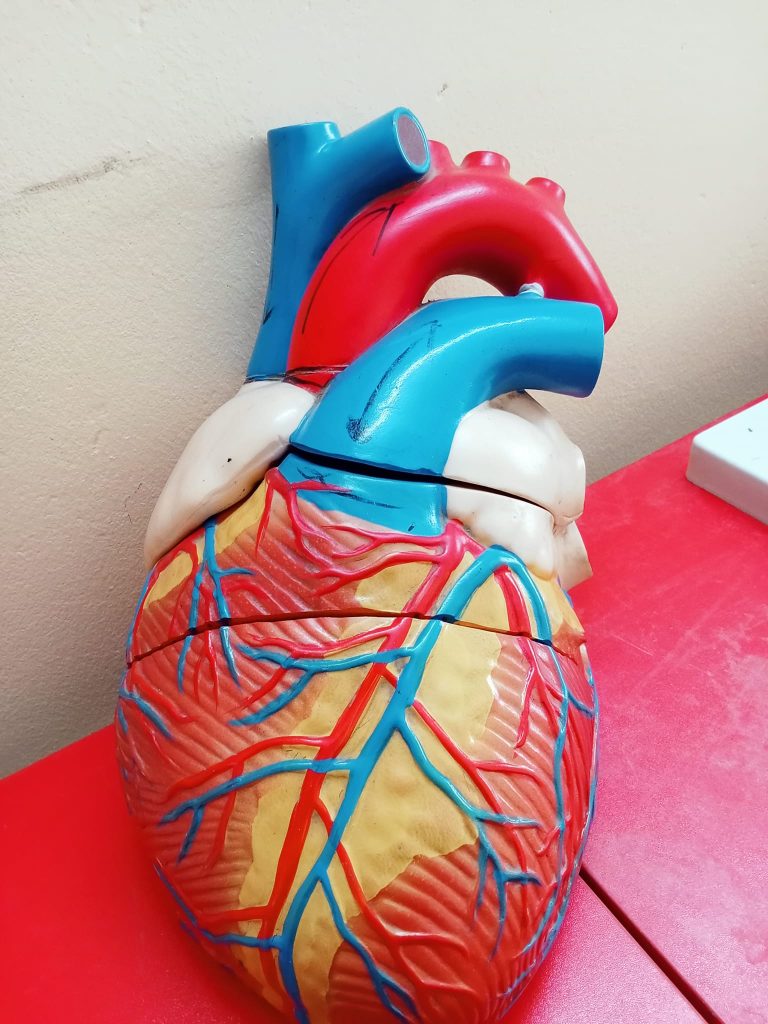
Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology
1. Introduction
The cardiovascular system is responsible for:
- Transport of oxygen, nutrients, hormones
- Removal of carbon dioxide & metabolic waste
- Regulation of body temperature, pH, and fluid balance
Main Components
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Arteries
- Veins
- Capillaries
- Blood
2. Anatomy of the Heart
Location
- Middle mediastinum of thoracic cavity
- Between lungs
- Apex points left at 5th intercostal space
Size & Shape
- Roughly the size of a closed fist
- Cone-shaped muscular organ
3. Layers of the Heart Wall
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Epicardium | Outer protective layer |
| Myocardium | Thick muscular layer (contracts) |
| Endocardium | Inner lining, smooth surface |
4. Chambers of the Heart
| Chamber | Function |
|---|---|
| Right Atrium (RA) | Receives deoxygenated blood from body |
| Right Ventricle (RV) | Pumps blood to lungs |
| Left Atrium (LA) | Receives oxygenated blood from lungs |
| Left Ventricle (LV) | Pumps blood to whole body |
👉 Left ventricle has the thickest wall (highest pressure).
5. Heart Valves
| Valve | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Tricuspid | RA → RV | Prevents backflow |
| Pulmonary | RV → Pulmonary artery | Prevents backflow |
| Mitral (Bicuspid) | LA → LV | Prevents backflow |
| Aortic | LV → Aorta | Prevents backflow |
6. Blood Supply of the Heart (Coronary Circulation)
Coronary Arteries
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
- Left Coronary Artery (LCA)
- Left Anterior Descending (LAD)
- Circumflex (LCX)
⚠️ Blockage → Ischemic heart disease / MI
7. Conducting System of the Heart
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| SA node | Natural pacemaker |
| AV node | Delays impulse |
| Bundle of His | Conducts impulse |
| Purkinje fibers | Ventricular contraction |
8. Blood Vessels Anatomy
Arteries
- Thick, elastic walls
- Carry blood away from heart
Veins
- Thin walls, valves present
- Carry blood toward heart
Capillaries
- One-cell thick
- Exchange of gases & nutrients
9. Physiology of the Heart
Cardiac Cycle
Two phases:
- Systole – contraction
- Diastole – relaxation
Heart Rate (HR)
- Normal adult: 60–100 beats/min
Stroke Volume (SV)
- Blood pumped per beat ≈ 70 mL
Cardiac Output (CO)
CO=HR×SV
Normal ≈ 5 L/min
10. Blood Pressure
| Type | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Systolic | 120 mmHg |
| Diastolic | 80 mmHg |
Controlled by:
- Cardiac output
- Peripheral resistance
- Blood volume
11. Regulation of Heart Activity
Neural Control
- Sympathetic → increases HR & force
- Parasympathetic (Vagus) → decreases HR
Hormonal Control
- Adrenaline
- Noradrenaline
- Thyroxine
12. Physiology of Blood Circulation
Pulmonary Circulation
Heart → Lungs → Heart
(Oxygenation of blood)
Systemic Circulation
Heart → Body → Heart
(Nutrient & oxygen delivery)
Cardiovascular Drugs & Pharmacology
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular drugs are medicines used to:
- Treat heart diseases
- Control blood pressure
- Manage heart rhythm
- Improve cardiac output
- Prevent thrombosis
2. Antihypertensive Drugs
A. Diuretics
Mechanism: Increase urine output → ↓ blood volume → ↓ BP
| Drug | Example |
|---|---|
| Thiazide | Hydrochlorothiazide |
| Loop | Furosemide |
| K⁺ sparing | Spironolactone |
Uses: Hypertension, heart failure
Side effects: Electrolyte imbalance
B. Beta-Blockers (β-blockers)
Mechanism: ↓ Heart rate & contractility
| Drug | Selectivity |
|---|---|
| Propranolol | Non-selective |
| Atenolol | β1-selective |
| Metoprolol | β1-selective |
Uses: HTN, angina, arrhythmia, MI
Side effects: Bradycardia, fatigue
C. ACE Inhibitors
Mechanism: Block Angiotensin-II → Vasodilation
| Drug |
|---|
| Enalapril |
| Captopril |
| Lisinopril |
Uses: HTN, heart failure, diabetic nephropathy
Side effects: Dry cough, hyperkalemia
D. ARBs
Mechanism: Block Angiotensin-II receptors
| Drug |
|---|
| Losartan |
| Valsartan |
Advantage: No cough
Uses: Same as ACE inhibitors
E. Calcium Channel Blockers (CCB)
Mechanism: ↓ Ca²⁺ entry → vasodilation
| Drug | Type |
|---|---|
| Amlodipine | Dihydropyridine |
| Verapamil | Non-DHP |
| Diltiazem | Non-DHP |
Uses: HTN, angina, arrhythmia
Side effects: Edema, constipation
3. Anti-Anginal Drugs
A. Nitrates
Mechanism: Venodilation → ↓ preload
| Drug |
|---|
| Nitroglycerin |
| Isosorbide dinitrate |
Uses: Angina pectoris
Side effects: Headache, hypotension
B. Beta-Blockers & CCBs
- Reduce myocardial oxygen demand
4. Drugs Used in Heart Failure
| Drug Class | Example |
|---|---|
| Diuretics | Furosemide |
| ACE inhibitors | Enalapril |
| Beta-blockers | Carvedilol |
| Cardiac glycosides | Digoxin |
Digoxin
Mechanism: ↑ Force of contraction
Uses: Heart failure, AF
Toxicity: Nausea, arrhythmia
5. Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs
Vaughan-Williams Classification
| Class | Drug |
|---|---|
| Class I | Lidocaine |
| Class II | Beta-blockers |
| Class III | Amiodarone |
| Class IV | Verapamil |
Uses: Atrial & ventricular arrhythmias
6. Anticoagulants
| Drug | Use |
|---|---|
| Heparin | Acute thrombosis |
| Warfarin | Long-term prevention |
| Dabigatran | Oral anticoagulant |
Side effect: Bleeding
7. Antiplatelet Drugs
| Drug |
|---|
| Aspirin |
| Clopidogrel |
Uses: MI, stroke prevention
8. Thrombolytic (Fibrinolytic) Drugs
| Drug |
|---|
| Streptokinase |
| Alteplase |
Uses: Acute MI, PE
Risk: Severe bleeding
9. Hypolipidemic Drugs
Statins
Mechanism: ↓ LDL cholesterol
| Drug |
|---|
| Atorvastatin |
| Rosuvastatin |
Uses: Prevention of atherosclerosis
Side effects: Muscle pain, liver injury
10. Emergency Cardiovascular Drugs
| Drug | Use |
|---|---|
| Adrenaline | Cardiac arrest |
| Atropine | Bradycardia |
| Dopamine | Shock |
Management of Hypertension & Hypotension
Management of Hypertension & Hypotension
PART A: MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION
1. Definition
Hypertension (HTN)
Persistent blood pressure ≥ 140/90 mmHg (on repeated measurements).
2. Goals of Management
- Reduce blood pressure
- Prevent target organ damage
- Reduce risk of stroke, MI, kidney failure
3. Non-Pharmacological Management (Lifestyle Modification)
A. Diet
- Low-salt diet (<5 g/day)
- DASH diet (fruits, vegetables, low fat)
- Reduce saturated fat
B. Weight Control
- BMI < 25 kg/m²
C. Physical Activity
- Brisk walking 30–45 min/day
D. Avoid Risk Factors
- Stop smoking
- Limit alcohol
- Stress management
4. Pharmacological Management of Hypertension
First-Line Drugs
| Drug Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Diuretics | Hydrochlorothiazide |
| ACE inhibitors | Enalapril |
| ARBs | Losartan |
| Calcium channel blockers | Amlodipine |
| Beta-blockers | Atenolol |
Stepwise Treatment
- Start with single drug
- Increase dose if BP not controlled
- Combine 2–3 drugs if needed
Special Situations
| Condition | Preferred Drug |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | ACEI / ARB |
| Heart failure | ACEI + Diuretic |
| Pregnancy | Methyldopa |
| Elderly | CCB / Diuretic |
5. Management of Hypertensive Emergency
BP ≥ 180/120 mmHg + organ damage
Drugs Used (IV)
- Nitroglycerin
- Labetalol
- Sodium nitroprusside
⚠️ BP should be reduced gradually, not suddenly.
PART B: MANAGEMENT OF HYPOTENSION
6. Definition
Hypotension
Systolic BP < 90 mmHg or symptomatic low BP.
7. Causes
- Dehydration
- Blood loss
- Shock
- Heart failure
- Drugs (antihypertensives)
8. Goals of Management
- Restore blood pressure
- Maintain organ perfusion
- Treat underlying cause
9. Non-Pharmacological Management
Immediate Measures
- Lay patient supine
- Elevate legs (Trendelenburg position)
- Ensure airway & oxygen
Fluid Therapy
- Oral fluids (mild cases)
- IV normal saline / Ringer’s lactate
10. Pharmacological Management of Hypotension
| Drug | Use |
|---|---|
| Dopamine | Shock |
| Noradrenaline | Severe hypotension |
| Adrenaline | Cardiac arrest |
| Midodrine | Chronic hypotension |
11. Management of Orthostatic Hypotension
- Slow position change
- Adequate hydration
- Compression stockings
- Fludrocortisone (if needed)
12. Monitoring & Nursing Care
- Regular BP monitoring
- Intake–output chart
- Electrolyte balance
- Patient education
13. Comparison Table (Exam Favorite)
| Feature | Hypertension | Hypotension |
|---|---|---|
| BP | High | Low |
| Main risk | Stroke, MI | Shock, syncope |
| Treatment | BP lowering drugs | Fluids & vasopressors |
Cardio Conductive System
1. Definition
The cardiac conductive system is a specialized network of muscle fibers that:
- Generates electrical impulses
- Conducts impulses through the heart
- Produces coordinated atrial and ventricular contraction
2. Components of the Cardiac Conductive System
1️⃣ Sinoatrial (SA) Node
- Location: Right atrium, near opening of superior vena cava
- Function: Natural pacemaker of the heart
- Rate: 60–100 impulses/min
✅ Initiates each heartbeat
2️⃣ Internodal Pathways
- Carry impulse from SA node → AV node
- Include anterior, middle, and posterior tracts
3️⃣ Atrioventricular (AV) Node
- Location: Interatrial septum, near tricuspid valve
- Function: Delays impulse (~0.1 sec)
- Rate: 40–60 impulses/min
✅ Allows ventricles to fill before contraction
4️⃣ Bundle of His (AV Bundle)
- Connects atria and ventricles
- Only normal electrical connection between them
5️⃣ Right & Left Bundle Branches
- Run along interventricular septum
- Left bundle divides into anterior & posterior fascicles
6️⃣ Purkinje Fibers
- Spread throughout ventricular myocardium
- Rate: 15–40 impulses/min
- Cause rapid, powerful ventricular contraction
3. Sequence of Electrical Conduction (Flowchart)
SA node → Atria → AV node → Bundle of His → Bundle branches → Purkinje fibers → Ventricles
4. Blood Supply of Conductive System (Clinical Point)
| Structure | Blood Supply |
|---|---|
| SA node | Right coronary artery (60%) |
| AV node | Right coronary artery |
| Bundle branches | LAD artery |
5. Physiology of Cardiac Conduction
Automaticity
Ability to generate impulse spontaneously
Conductivity
Ability to transmit impulse
Excitability
Ability to respond to stimulus
Contractility
Ability to contract
6. ECG Correlation (Very Important)
| ECG Wave | Event |
|---|---|
| P wave | Atrial depolarization |
| PR interval | AV nodal delay |
| QRS complex | Ventricular depolarization |
| T wave | Ventricular repolarization |
7. Clinical Disorders of Conductive System
Arrhythmias
- Bradycardia
- Tachycardia
- Atrial fibrillation
Heart Blocks
| Type | Problem |
|---|---|
| 1st degree | Prolonged PR |
| 2nd degree | Dropped beats |
| 3rd degree | Complete block |
Heart Block (Coronary & Conductive Block)
1. Definition
Heart block is a disorder of the cardiac conduction system where electrical impulse conduction is delayed or completely blocked, usually at the AV node or bundle branches.
2. Causes of Heart Block
Common Causes
- Ischemic heart disease / MI
- Degenerative changes (elderly)
- Drugs (β-blockers, digoxin, CCBs)
- Electrolyte imbalance (↑ K⁺)
- Congenital heart disease
- Myocarditis
3. Types of Heart Block (Very Important)
A. Atrioventricular (AV) Block
- First-degree AV block
- Second-degree AV block
- Mobitz type I (Wenckebach)
- Mobitz type II
- Third-degree AV block (Complete block)
4. First-Degree AV Block
Definition
- Delayed conduction through AV node
- All impulses reach ventricles
ECG Finding
- PR interval > 0.20 sec
- Every P wave followed by QRS
Clinical Features
- Usually asymptomatic
Management
- No treatment required
- Observe & remove offending drugs
5. Second-Degree AV Block
(a) Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach)
Mechanism: Progressive AV nodal delay
ECG
- PR interval gradually lengthens
- Eventually one QRS is dropped
Symptoms
- Mild dizziness
- Often asymptomatic
Management
- Usually benign
- Atropine if symptomatic
(b) Mobitz Type II
Mechanism: Sudden conduction failure below AV node
ECG
- Fixed PR interval
- Sudden dropped QRS
⚠️ More dangerous than type I
Symptoms
- Syncope
- Severe bradycardia
Management
- Permanent pacemaker required
6. Third-Degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block)
Definition
- No impulse conduction from atria to ventricles
- Atria and ventricles beat independently
ECG
- P waves & QRS complexes completely dissociated
- Ventricular rate very slow
Symptoms
- Severe bradycardia
- Dizziness
- Syncope (Stokes-Adams attack)
- Heart failure
Management
- Emergency: Atropine / temporary pacing
- Definitive: Permanent pacemaker
7. Bundle Branch Block (BBB)
Types
- Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
ECG Clue
- Wide QRS complex (>0.12 sec)
Significance
- LBBB often indicates serious heart disease
8. Comparison Table (Exam Favorite)
| Feature | 1st Degree | 2nd Degree | 3rd Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| PR interval | Prolonged | Variable | No relation |
| Dropped beats | No | Yes | Complete |
| Severity | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| Pacemaker | No | Sometimes | Yes |
9. Nursing & Clinical Management
- Monitor ECG & heart rate
- Observe for syncope
- Maintain airway & oxygen
- Prepare for pacemaker if needed
 HRTD Medical Institute HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute HRTD Medical Institute

